本次作业只有两个Part,但是难度上升很多,我做的结果也有点小问题,需要后续修改。
Part 1: 静态逆向运动学
课程中介绍了很多中IK的算法,最简单的是Cyclic Coordinate Descent(CCD),复杂一点的有Gradient Descent、Gauss Newton Method、Damped Gauss Newton Method等。课程中还提到了额外的FABRIK算法等。我在作业中主要实现了前4种方法,其中后三种方法差距不大。
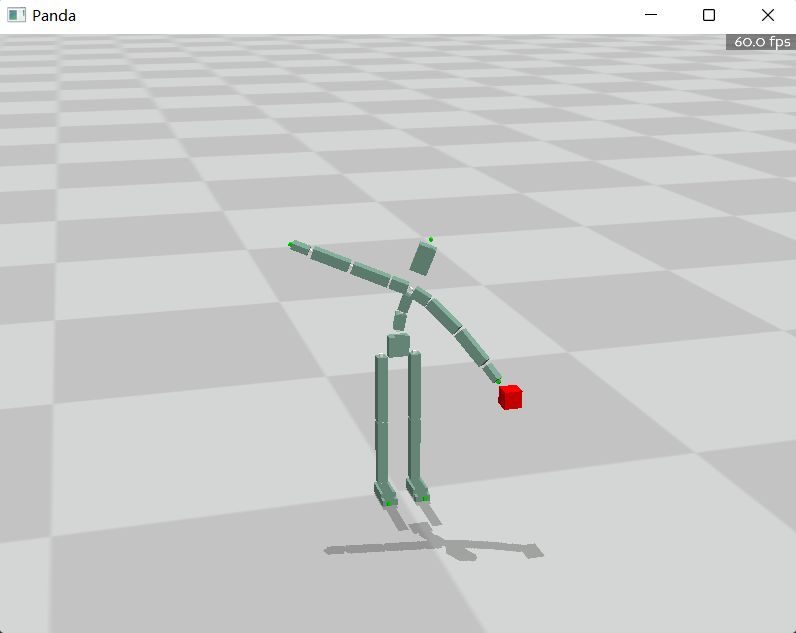
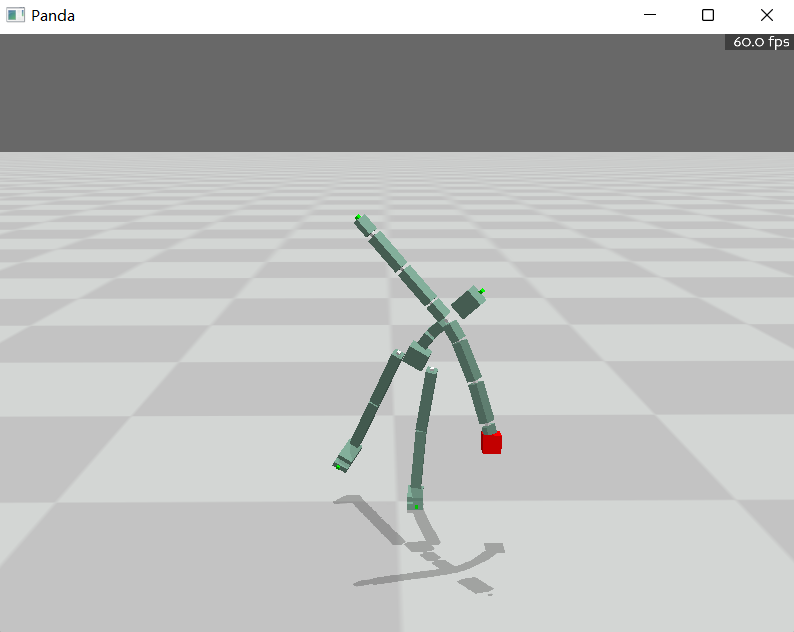
CCD
def cyclicCoordinateDescent(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations, target_pose):
# 计算 inverse_kinematics 链的信息
path_offsets, path_positions, path_orientations = getJointPathInfo(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations)
# CCD 循环
cnt = 0
end_index = meta_data.path_name.index(meta_data.end_joint)
while (np.linalg.norm(joint_positions[meta_data.path[end_index]] - target_pose) >= 1e-2 and cnt <= 10):
for i in range(end_index):
current_index = end_index - i - 1
current_position = path_positions[current_index]
end_position = path_positions[end_index]
# delta
vector_current2end = end_position - current_position
vector_current2target = target_pose - current_position
current2end = vector_current2end / np.linalg.norm(vector_current2end)
current2target = vector_current2target / np.linalg.norm(vector_current2target)
# 计算轴角
rotation_radius = np.arccos(np.clip(np.dot(current2end, current2target), -1, 1))
current_axis = np.cross(current2end, current2target)
rotation_axis = current_axis / np.linalg.norm(current_axis)
rotation_vector = R.from_rotvec(rotation_radius * rotation_axis)
# 计算方位与位置
path_orientations[current_index] = rotation_vector * path_orientations[current_index]
path_rotations = []
path_rotations.append(path_orientations[0])
# update joint rotations R_{i} = Q_{i-1}^T Q_{i}
for j in range(len(path_orientations) - 1):
path_rotations.append(R.inv(path_orientations[j]) * path_orientations[j + 1])
for j in range(current_index, end_index):
path_positions[j + 1] = path_positions[j] + path_orientations[j].apply(path_offsets[j + 1])
if j + 1 < end_index:
path_orientations[j + 1] = path_orientations[j] * path_rotations[j + 1]
else:
path_orientations[j + 1] = path_orientations[j]
cnt += 1
return path_positions, path_orientations
def applyJointIKToAll(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations, path_positions, path_orientations):
# print(meta_data.path)
# print(meta_data.path1)
# print(meta_data.path2)
# print(path_orientations)
# 计算 path_joints 的 rotation
joint_rotations = R.identity(len(meta_data.joint_name))
for i in range(len(meta_data.joint_parent)):
if meta_data.joint_parent[i] == -1:
joint_rotations[i] = R.from_quat(joint_orientations[i])
else:
joint_rotations[i] = R.inv(R.from_quat(joint_orientations[meta_data.joint_parent[i]])) * R.from_quat(joint_orientations[i])
# # apply IK rotation result
if len(meta_data.path2) > 1: # we have locked sub chain
# path_joints 的 forward_kinematics
# have to set {i}'s joint orientation with {i-1}' orientation
# because end's joint is not a valid joint
for i in range(len(meta_data.path2) - 1):
joint_orientations[meta_data.path2[i + 1]] = path_orientations[i].as_quat()
joint_orientations[meta_data.path2[-1]] = path_orientations[len(meta_data.path2) - 1].as_quat()
for i in range(len(meta_data.path1) - 1):
joint_orientations[meta_data.path[i + len(meta_data.path2)]] = path_orientations[i + len(meta_data.path2)].as_quat()
else: # we don't have locked sub chain
# path_joints 的 forward_kinematics
for j in range(len(meta_data.path)):
joint_orientations[meta_data.path[j]] = path_orientations[j].as_quat()
# apply IK position result
for i in range(len(meta_data.path)):
joint_positions[meta_data.path[i]] = path_positions[i]
# 其余 joints 的 forward_kinematics
for i in range(len(meta_data.joint_parent)):
if meta_data.joint_parent[i] == -1:
continue
if meta_data.joint_name[i] not in meta_data.path_name:
joint_positions[i] = joint_positions[meta_data.joint_parent[i]] + \
R.from_quat(joint_orientations[meta_data.joint_parent[i]]).apply(meta_data.joint_initial_position[i] - \
meta_data.joint_initial_position[meta_data.joint_parent[i]])
joint_orientations[i] = (R.from_quat(joint_orientations[meta_data.joint_parent[i]]) * joint_rotations[i]).as_quat()
return joint_positions, joint_orientations
def part1_inverse_kinematics(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations, target_pose):
"""
完成函数,计算逆运动学
输入:
meta_data: 为了方便,将一些固定信息进行了打包,见上面的meta_data类
joint_positions: 当前的关节位置,是一个numpy数组,shape为(M, 3),M为关节数
joint_orientations: 当前的关节朝向,是一个numpy数组,shape为(M, 4),M为关节数
target_pose: 目标位置,是一个numpy数组,shape为(3,)
输出:
经过IK后的姿态
joint_positions: 计算得到的关节位置,是一个numpy数组,shape为(M, 3),M为关节数
joint_orientations: 计算得到的关节朝向,是一个numpy数组,shape为(M, 4),M为关节数
"""
path_positions, path_orientations = cyclicCoordinateDescent(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations, target_pose)
joint_positions, joint_orientations = applyJointIKToAll(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations, path_positions, path_orientations)
return joint_positions, joint_orientations
基于Jacobian矩阵的方法:
def calculateJointAngle(path_orientations):
path_rotations = []
path_rotations.append(path_orientations[0])
# update joint rotations R_{i} = Q_{i-1}^T Q_{i}
for j in range(len(path_orientations) - 1):
rot = R.inv(path_orientations[j]) * path_orientations[j + 1]
path_rotations.append(rot)
# decompose euler angle
joint_angle = []
for r in path_rotations:
eula = R.from_matrix(r.as_matrix()).as_euler('XYZ', degrees=True)
joint_angle.append(eula)
return joint_angle
def calculateJacobian(end_position, joint_angle, path_positions, path_orientations):
# fill jacobian matrix
# i'th column = a_{i} x r{i}
# for XYZ ball joint, use Euler angle to decomposite: R = Rx Ry Rz
jacobian = []
print("----")
print(end_position)
print("----")
for i in range(len(joint_angle)):
# print(path_positions[i], joint_angle[i+1])
current_position = path_positions[i]
current_angle = joint_angle[i]
r = current_position - end_position
rx = R.from_euler('XYZ', [current_angle[0], 0., 0.], degrees=True)
rxy = R.from_euler('XYZ', [current_angle[0], current_angle[1], 0.], degrees=True)
q_prev = None
if i == 0:
q_prev = R.from_quat([ 0. , 0.80976237, 0.53984158, -0.22990426])
else:
q_prev = path_orientations[i-1]
ax = q_prev.apply(np.array([1., 0., 0.]).reshape(-1, 3))
ay = q_prev.apply(rx.apply(np.array([0., 1., 0.]).reshape(-1, 3)))
az = q_prev.apply(rxy.apply(np.array([0., 0., 1.]).reshape(-1, 3)))
jacobian.append(np.cross(ax, r))
jacobian.append(np.cross(ay, r))
jacobian.append(np.cross(az, r))
jacobian = np.concatenate(jacobian, axis=0).transpose()
return jacobian
def calculateJointPathInJacobian(theta, end_index, path_offsets, path_positions, path_orientations):
path_rotations = []
theta = theta.reshape(-1,3)
for i in range(len(theta)):
eula = theta[i]
path_rotations.append(R.from_euler('XYZ', eula, degrees=True))
print(end_index, len(path_positions), len(path_rotations))
# update joint rotations R_{i} = Q_{i-1}^T Q_{i}
# path_orientations[0] = path_rotations[0]
for j in range(end_index):
path_positions[j + 1] = path_positions[j] + path_orientations[j].apply(path_offsets[j + 1])
if j + 1 < end_index:
path_orientations[j + 1] = path_orientations[j] * path_rotations[j + 1]
else:
path_orientations[j + 1] = path_orientations[j]
return path_positions, path_orientations
def gradientDescent(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations, target_pose):
# 计算 inverse_kinematics 链的信息
path_offsets, path_positions, path_orientations = getJointPathInfo(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations)
end_index = meta_data.path_name.index(meta_data.end_joint)
count = 0
alpha = 16
while (np.linalg.norm(joint_positions[meta_data.path[end_index]] - target_pose) >= 1e-2 and count <= 10):
end_position = path_positions[end_index]
joint_angle = calculateJointAngle(path_orientations)
jacobian = calculateJacobian(end_position, joint_angle, path_positions, path_orientations)
delta = np.array(target_pose - end_position).reshape(3, -1)
# get all path rotations, convert to XYZ euler angle
theta = np.concatenate(joint_angle, axis=0).transpose().reshape(-1, 1)
# theta_i+1 = theta_i - alpha J^T delta
delta = alpha * np.dot(jacobian.transpose(), delta)
print(theta.transpose())
print(theta.shape)
print(delta.transpose())
print(delta.shape)
theta = theta - delta
# convert theta back to rotations
path_positions, path_orientations = calculateJointPathInJacobian(theta, end_index, path_offsets, path_positions, path_orientations)
alpha = alpha * 0.8
count = count + 1
return path_positions, path_orientations
def gaussNewtonMethod(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations, target_pose):
# 计算 inverse_kinematics 链的信息
path_offsets, path_positions, path_orientations = getJointPathInfo(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations)
end_index = meta_data.path_name.index(meta_data.end_joint)
count = 0
alpha = 15
while (np.linalg.norm(joint_positions[meta_data.path[end_index]] - target_pose) >= 1e-2 and count <= 10):
end_position = path_positions[end_index]
joint_angle = calculateJointAngle(path_orientations)
jacobian = calculateJacobian(end_position, joint_angle, path_positions, path_orientations)
delta = np.array(target_pose - end_position).reshape(3, -1)
# get all path rotations, convert to XYZ euler angle
theta = np.concatenate(joint_angle, axis=0).transpose().reshape(-1, 1)
# theta = theta_0 - alpha J^T (JJ^T)^-1 delta
temp = np.linalg.inv(np.dot(jacobian, jacobian.transpose()))
temp = np.dot(jacobian.transpose(), temp)
delta = alpha * np.dot(temp, delta)
theta = theta - delta
# convert theta back to rotations
path_positions, path_orientations = calculateJointPathInJacobian(theta, end_index, path_offsets, path_positions, path_orientations)
alpha = alpha * 0.95
count = count + 1
return path_positions, path_orientations
def dampedGaussNewtonMethod(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations, target_pose):
# 计算 inverse_kinematics 链的信息
path_offsets, path_positions, path_orientations = getJointPathInfo(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations)
# theta = theta_0 - alpha J^T (JJ^T + lambda W)^-1 delta
end_index = meta_data.path_name.index(meta_data.end_joint)
count = 0
alpha = 15
lambda_ = 0.05
while (np.linalg.norm(joint_positions[meta_data.path[end_index]] - target_pose) >= 1e-2 and count <= 10):
end_position = path_positions[end_index]
joint_angle = calculateJointAngle(path_orientations)
jacobian = calculateJacobian(end_position, joint_angle, path_positions, path_orientations)
delta = np.array(target_pose - end_position).reshape(3, -1)
# get all path rotations, convert to XYZ euler angle
theta = np.concatenate(joint_angle, axis=0).transpose().reshape(-1, 1)
# theta = theta_0 - alpha J^T (JJ^T + lambda W)^-1 delta
temp_1 = np.dot(jacobian, jacobian.transpose())
temp_1 = temp_1 + lambda_ * np.ones(temp_1.shape)
temp = np.linalg.inv(temp_1)
temp = np.dot(jacobian.transpose(), temp)
delta = alpha * np.dot(temp, delta)
theta = theta - delta
# convert theta back to rotations
path_positions, path_orientations = calculateJointPathInJacobian(theta, end_index, path_offsets, path_positions, path_orientations)
alpha = alpha * 0.95
count = count + 1
return path_positions, path_orientations
我写的Jacobian方法里有点小问题,具体来说就是对于Part 2的作业无法适用,但是在静态解算时并没有问题。
Part 2: 逆向运动学+bvh
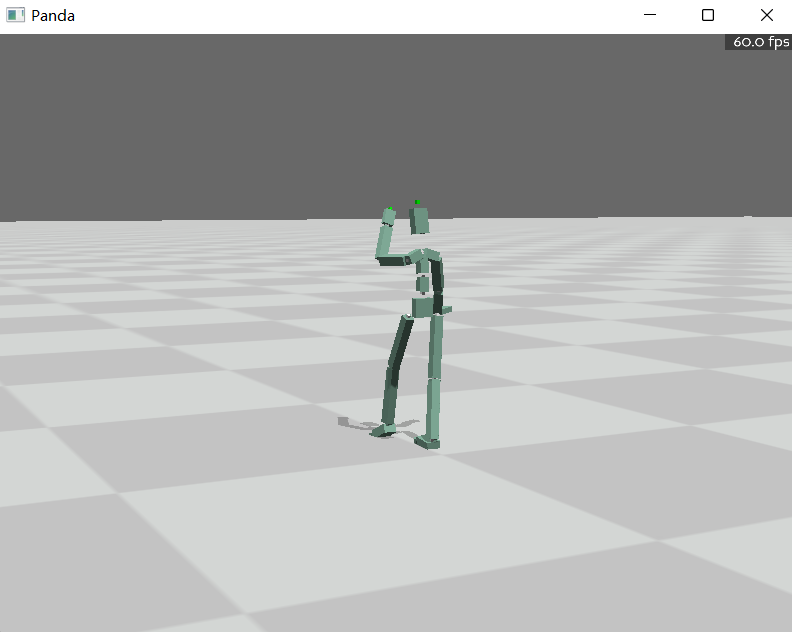
可以看到,作业1中走路的小人变成了看手机走路,说明IK成功。
def part2_inverse_kinematics(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations, relative_x, relative_z, target_height):
"""
输入lWrist相对于RootJoint前进方向的xz偏移,以及目标高度,IK以外的部分与bvh一致
"""
target_pose = np.array([joint_positions[0][0] + relative_x, target_height, joint_positions[0][2] + relative_z])
path_positions, path_orientations = cyclicCoordinateDescent(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations, target_pose)
joint_positions, joint_orientations = applyJointIKToAll(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations, path_positions, path_orientations)
return joint_positions, joint_orientations
Part 3(选做): 两个目标的逆向运动学
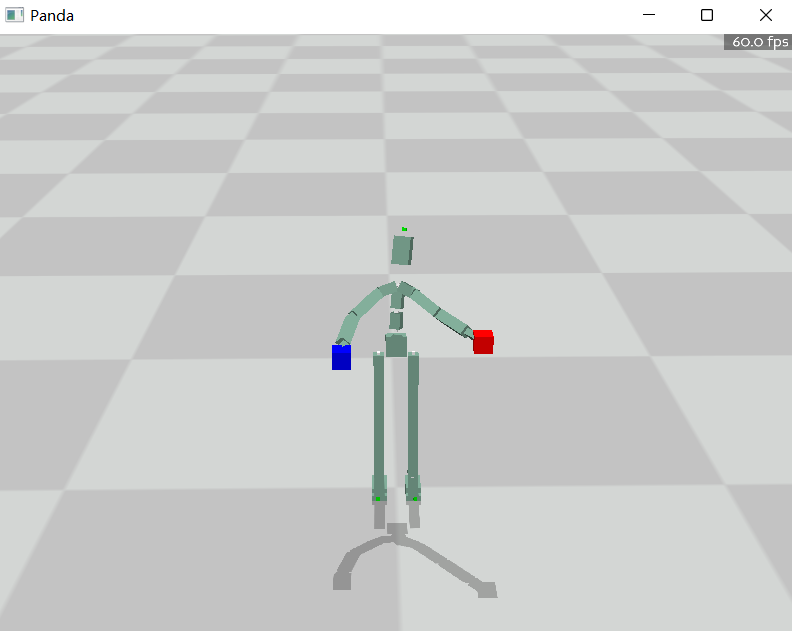
这个部分作业我选择了一个暴力迭代的方法,不论怎么样,就迭代10轮,CCD与Jacobian方法均可得到比较好的效果。CCD方法比Jacobian方法还是快很多。
def bonus_inverse_kinematics(meta_data, joint_positions, joint_orientations, left_target_pose, right_target_pose):
"""
输入左手和右手的目标位置,固定左脚,完成函数,计算逆运动学
"""
count = 0
while count < 10:
# left target
meta_data_l = MetaData(meta_data.joint_name, meta_data.joint_parent, meta_data.joint_initial_position, 'RootJoint', 'lWrist_end')
path_positions_l, path_orientations_l = gradientDescent(meta_data_l, joint_positions, joint_orientations, left_target_pose)
joint_positions, joint_orientations = applyJointIKToAll(meta_data_l, joint_positions, joint_orientations, path_positions_l, path_orientations_l)
# right target
meta_data_r = MetaData(meta_data.joint_name, meta_data.joint_parent, meta_data.joint_initial_position, 'RootJoint', 'rWrist_end')
path_positions_r, path_orientations_r = gradientDescent(meta_data_r, joint_positions, joint_orientations, right_target_pose)
joint_positions, joint_orientations = applyJointIKToAll(meta_data_r, joint_positions, joint_orientations, path_positions_r, path_orientations_r)
count += 1
return joint_positions, joint_orientations